5G Network & differences between 2G, 3G, 4G, & 5G networks?
Last updated on March 25th, 2023 by A1 True Jobs
Simply, the "G" stands for "GENERATION". While connected to the internet, the speed of the connection depends upon the signal strength that is shown in abbreviations like 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, etc. on any mobile device. Each generation of wireless broadband is defined as a set of telephone network standards that describe the technological implementation of the system.
The aim of wireless communication is to provide high quality, reliable communication just like wired communication and each new generation represents a big leap in that direction. Mobile communication has become more popular in the last few years due to fast reform in mobile technology. For the comparison of 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G we first need to understand the key features of all these technologies.
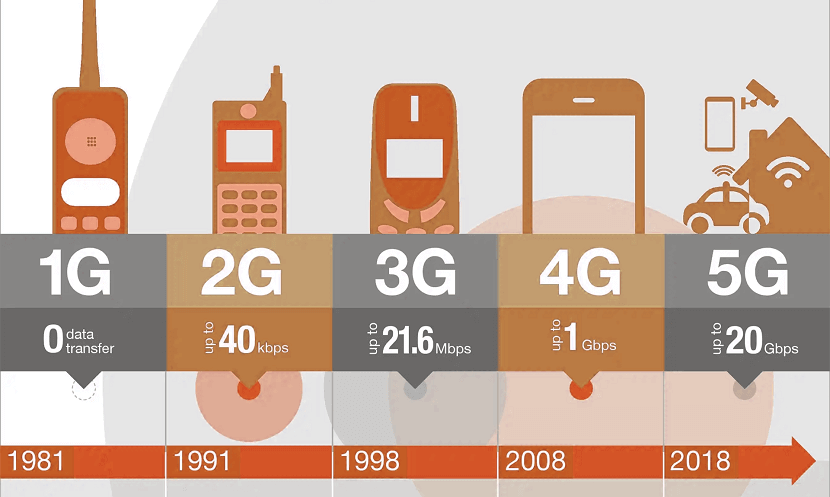
Comparison of 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G
| Comparison | 2G | 3G | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Introduced in Year | 1993 | 2001 | 2009 | 2018 |
| Technology | GSM | WCDMA | LTE, WiMAX | MIMO, mm Waves |
| Access System | TDMA, CDMA | CDMA | CDMA | OFDM, BDMA |
| Switching Type | Circuit Switching for Voice and Packet Switching for Data | Packet Switching Except for Air Interference | Packet Switching | Packet Switching |
| Internet Service | Narrowband | Broadband | Ultra Broadband | Wireless World Wide Web |
| Brandwidth | 25 MHz | 25 MHz | 100 MHz | 30 GHz to 300 GHz |
| Advantage | Multimedia Features (SMS, MMS), Internet Access and SIM Introduced | Speed, High Speed Handoffs, Global Mobility | Extremely High Speeds, Low Latency | |
| Applications | Voice Calls, Short Messages | Video Conferencing, Mobile TV, GPS | High Speed Applications, Mobile TV, Wearable Devices | High Resolution Video Streaming, Remote Control of Vehicles, Robots, and Medical Procedures |
What is 5G (FIFTH GENERATION)?
5G networks operate on rarely used radio millimeter bands in the 30 GHz to 300 GHz range. Testing of 5G range in mmWave has produced results approximately 500 meters from the tower. Using small cells, the deployment of 5G with millimetre wave based carriers can improve overall coverage area. Combined with beamforming, small cells can deliver extremely fast coverage with low latency.
Low latency is one of 5G’s most important features. 5G uses a scalable orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) framework. 5G benefits greatly from this and can have latency as low as one millisecond with realistic estimates to be around 1 – 10 seconds. 5G is estimated to be 60 to 120 times faster than the average 4G latency.
Active antenna 5G encapsulated with 5G massive MIMO is used for providing better connections and enhanced user experience. Big 5G array antennas are deployed to gain additional beamforming information and knock out propagation challenges that are experienced at mmWave frequency ranges.
Further, 5G networks clubbed with network slicing architecture enables telecom operators to offer on-demand tailored connectivity to their users that is adhered to Service Level Agreement (SLA). Such customised network capabilities comprise latency, data speed, latency, reliability, quality, services, and security.
With speeds of up to 10 Gbps, 5G is set to be as much as 10 times faster than 4G. Following is a brief comparison of 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G.
What is 4G (FOURTH GENERATION)?
The main difference between 3G and 4G is the data rate. There is also a huge difference between 3G and 4G technology. The key technologies that have made 4G possible are MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) and OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing). The most important 4G standards are WiMAX and LTE. While 4G LTE is a major improvement over 3G speeds, it is technically not 4G. What is the difference between 4G and LTE?
Even after it was widely available, many networks were not up to the required speed of 4G. 4G LTE is a “fourth generation long term evolution”, capable of delivering a very fast and secure internet connection. Basically, 4G is the predetermined standard for mobile network connections. 4G LTE is the term given to the path which has to be followed to achieve those predefined standards. Some of the features of 4G LTE are:
- Support interactive multimedia, voice, video.
- High speed, high capacity and low cost per bit (Speeds of up to 20 Mbps or more.)
- Global and scalable mobile networks.
- Ad hoc and multi-hop networks.
How is 5G different from 4G?
| 5G | 4G |
|---|---|
| 5G uses utilises much higher radio frequencies of 28 GHz. | 4G uses lower reading frequencies of 700 MHz to 2500 MHz. |
| 5G transfers more data over the air at faster speeds. | 4G speed is lesser with less data transfer. |
| 5G has lower latency i.e the delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction. Latency for 5G is predicted to be below 10 milliseconds, and in best cases around 1 millisecond. | 4G has higher latency as compared to 5G. Latency for 4G is around 20-30 milliseconds. |
| 5G uses millimetre wave spectrum which enables more devices to be used within the same geographic area supporting around one million per square kilometre. | 4G supports a lesser number of devices of about 4,000 devices per square kilometre. |
| 5G uses a new digital technology that improves coverage, speed and capacity. | 4G has led to more congestion and lesser coverage as compared to 5G. |
How is 5G technology important for India?
1. High speed and digital India: 5G will revolutionise the mobile experience with speedy wireless network, which can support up to 10 to 20 GBPS of data download speed. Compared to conventional mobile transmission technologies, voice and high-speed data can be simultaneously transferred efficiently in 5G. This will enhance and support the government's effort to promote digital India.
2. Better Governance: Better speed and connectivity would reduce red tapism. It will enhance speedy completion of projects and better implementation of policies. It will enable accountability in the system through a better monitoring system and will reduce corruption.
3. Low latency: It is one of the most important features of 5G technology which is significant for autonomous driving and mission critical applications. 5G networks are capable of latency less than a millisecond. This help in logistics improvement and would reduce overall cost of goods and services.
4. Employment generation: 5G wireless technology will open greater opportunities for new device manufactures and application developers. New VoIP devices and smart devices will be introduced in the market and thus more job opportunities as well. This will help in inclusive growth reaping demographic dividends.
5. Enhanced network coverage: Device-to-device communication techniques will further enhance network performance and support during limited access or absence of mobile networks. Small cell concepts used in 5G will have multiple advantages of better cell coverage, maximum data transfer, low power consumption and cloud access network etc. This will help in reducing the digital gap in India.
6. Entertainment and multimedia industry: Analysts found that 55% of mobile Internet traffic has been used for video downloads globally in 2015. This trend will increase in future and high definition video streaming will be common in future. This will help in growth of entertainment industry and thus more jobs will be there. It will also increase government revenue.
7. Enhanced Security: 5G wireless technology is one the best solution for security surveillance due to higher bandwidth and unlicensed spectrum. It will enhance better coordination among various agencies. Smart appliances which can be configured and accessed from remote locations, closed circuit cameras will provide high quality real-time video for security purposes.
8. Logistics and shipping: The logistics and shipping industry can make use of smart 5G technology for goods tracking, fleet management, centralised database management, staff scheduling and real-time delivery tracking and reporting.
9. Smart cities: It will fuel the government's smart city project. Smart city applications like traffic management, instant weather update, local area broadcasting, energy management, smart power grid, smart lighting of street, water resource management, crowd management, emergency response etc. can use reliable 5G wireless network for its functioning.
10. Industrial Growth: Future industries will depend on smart wireless technologies like 5G and LTE advanced for efficient automation of equipment, maintenance, safety, tracking, smart packing, shipping, logistics and energy management.
11. Agricultural applications: 5g technology can be used for agriculture and smart farming in future. Using smart RFID sensors and GPS technology, farmers can track the location of livestock and manage them easily. Smart sensors can be used for irrigation control, Cisco CCNA Certification access control and energy management.
12. Healthcare and mission critical applications: 5G technology will support medical practitioners to perform advanced medical procedures with reliable wireless networks connected to another side of the globe. Doctors can connect with patients from anywhere anytime and advise them when necessary. Scientists are working on smart medical devices which can perform remote surgery. Smart medical devices like wearable devices will continuously monitor a patient's condition and activate alerts during an emergency.
India should not miss the opportunity and should proactively work to deploy 5g technology. We should focus on strengthening our cyber infrastructure. Funds should be allocated and local technology and telecom firms should be incentivised to develop their internal capacities which would in turn help 5G technology succeed in the country. 5g start-ups that enable this design and manufacturing capabilities should be promoted.
What is 3G (THIRD GENERATION)?
The 3G standard utilises Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) as its core network architecture. 3G network combines aspects of the 2G network with new technologies and protocols to deliver a significantly faster data rate. By using packet switching, the original technology was improved to allow speeds up to 14 Mbps. It used Wide Band Wireless Network that increased clarity. It operates at a range of 2100 MHz and has a bandwidth of 15-20 MHz. Some of the main features of 3G are:
- Speed of up to 2 Mbps
- Increased bandwidth and data transfer rates
- Send/receive large email messages
- Large capacities and broadband capabilities
What is 2G (SECOND GENERATION)?
2G refers to the second generation of mobile networks based on GSM. The radio signals used by the 1G network were analog, while 2G networks were digital. 2G capabilities were achieved by allowing multiple users on a single channel via multiplexing. During 2G, cellular phones were used for data along with voice. Some of the key features of 2G were:
- Data speeds of up to 64 kbps
- Use of digital signals instead of analog
- Enabled services such as SMS and MMS (Multimedia Message)
- Provided better quality voice calls
- It used a bandwidth of 30 to 200 KHz
2G vs 3G vs 4G vs 5G
Each generation in some way has improved over its predecessor. There is a lot of ground to compare the cell networks over. Following is the comparison between 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G.
The comparison of 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G clearly shows the differences in the technologies. The comparison of 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G also makes it evident that 5G is going to be one of the most ambitious leaps in the history of cell network technologies.
Disclaimer : The original content is 5G Network & differences between 2G, 3G, 4G, & 5G networks? and owner ( RGB Web Tech ) reserved rights for content
